SEO overview |
|
|

|
|
|
SEO overview |
|
|

|
|
|
|
||
Search engine optimization (SEO) is a process that attempts to improve the page rank of a website, which determines its organic position in the results of web search engines (such as Google). Being higher in these results benefits the site by naturally attracting more visitors.
While Kentico CMS cannot guarantee by itself that your website will have good search engine optimization, it provides many features that simplify related configuration tasks and make it easier to follow general best practices. Additionally, the system ensures a solid SEO foundation by generating pages with valid, standards compliant output code and URLs in a search engine friendly format.
|
Tracking search engine traffic
You can use the web analytics module to review the results of your website's SEO. It is possible to monitor user traffic gained from search engines and the activity of web crawlers on your site's pages can also be tracked.
For more information, please refer to the Monitoring traffic from search engines topic in the Modules -> Web analytics chapter of this guide. |
Editing the metadata of pages
An important SEO consideration is the metadata of individual pages, which you can edit by selecting the corresponding document in the content tree of CMS Desk and opening its Properties -> Metadata tab. Here you can set properties such as the page title or meta description.
See also: Content management -> Document properties -> Metadata
You can configure most of the SEO functionality of your website in the Site Manager -> Settings -> URLs and SEO interface. The settings here are divided into three main sections which are described below.
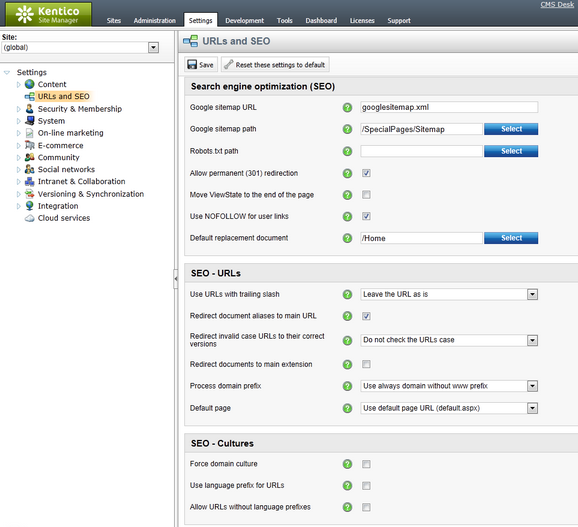
Before search engines can provide results that link users to your website, they need to index the site using web crawlers (robots). The settings in this section allow you to use standard techniques for giving instructions to crawlers. You can also enable several options that help crawlers easily and accurately index the pages on your website.
Google sitemap URL |
These two settings set up the URL of the website's Google (XML) sitemap and the path of the source document. The sitemap allows you to instruct web crawlers how to index the site's pages.
Please see the Google Sitemaps topic to learn more about using sitemaps in Kentico CMS. |
Google sitemap path |
|
Robots.txt path |
Specifies the path of the document that generates the website's robots.txt file.
Refer to Managing robots.txt for detailed information about setting up robots.txt content. |
Allow permanent (301) redirection |
If enabled, the system uses permanent (301) redirection instead of standard temporary (302) redirection. This is highly recommended, because it allows web crawlers to properly react to any changes made on your website and pass page rank to the new or main URL. |
Move ViewState to the end of the page |
If enabled, the system places the ViewState field at the end of the output code generated for pages. This helps search engine crawlers process more page content. |
Use NOFOLLOW for user links |
If enabled, the system instructs search engine crawlers not to follow links posted by users on Forums, Message boards or in Blog comments. This is achieved by including the rel="nofollow" attribute in the output code of all such link tags.
This can prevent damage to your website's search ranking caused by user‑generated links that lead to unrelated content. The setting can also help stop spammers from passing page rank to other sites. |
Default replacement document |
See the Assigning replacement documents for deleted pages section below. |
Assigning replacement documents for deleted pages:
Removing documents can have a negative effect on your website's traffic. Visitors may find it confusing if pages suddenly become unavailable (e.g. if they have a deleted page bookmarked). Another thing to consider is that deleted pages might be indexed by search engines, which then provide invalid links in their search results until they re‑index the site's content.
You can mitigate these problems by setting up other documents as replacements when deleting pages:
1. Select the document that you wish to remove in the CMS Desk content tree and click Delete.
oThe Delete document confirmation dialog opens.
2. Check the Display alternate page when visitors access the deleted document box.
3. Specify the path of the Replacement document.
oThe field loads its default value from the Default replacement document setting of the current website, but you can enter a different path for each specific case.
4. Enable or disable the following configuration options:
•Copy all paths - if checked, the website uses the replacement document for all possible URL paths of the deleted document (including any document aliases). If false, the replacement only covers the main URL of the deleted page, i.e. the corresponding document's custom URL path (if one is specified) or alias path.
•Include child nodes - if checked, the website uses the replacement document for all child documents removed along with the deleted page.
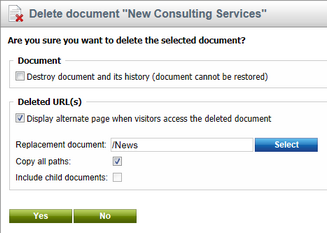
Setting a replacement document in the Delete document confirmation dialog
Once you confirm the deletion, the system automatically adds document aliases to the replacement document. These aliases ensure that the website serves up the replacement page whenever a visitor requests the URLs of the deleted document. When combined with permanent 301 redirection, the replacement aliases also properly inform search engine crawlers about the change in your website's structure.
The settings in this section allow you to configure URL rewriting that focuses on avoiding issues with duplicate content, i.e. having the same content available under multiple URLs. Such problems can have a negative effect on search ranking, so it is recommended to set up a unified URL format.
Use URLs with trailing slash |
Specifies how the rewriter handles trailing slashes in URLs. Possible options:
•Leave the URL as is •Always use URLs with a trailing slash •Always use URLs without a trailing slash |
Redirect document aliases to main URL |
Enabling this setting ensures that documents always have only one valid URL and other aliases are redirected to this main URL. The main URL of a document is determined either by its alias path, or custom URL path if one is specified.
Note: You can override this setting for individual document aliases through their Alias redirection property.
For more information about document URLs, see the Multiple document aliases topic. |
Redirect invalid case URLs to their correct versions |
Determines how the system handles the letter case of characters in URLs. Available options:
•Do not check the URL case •Use the exact URL of each document •Redirect all requests to lower case URLs •Redirect all requests to upper case URLs |
Redirect documents to main extension |
If enabled, the system ensures that all document URLs use the current main extension. The main URL extension is the first one specified in the Friendly URL extension setting. Any URLs with a different extension are automatically redirected to a corresponding URL with the main extension. |
Process domain prefix |
Determines how the rewriter handles the www domain prefix in the website's URLs. You can leave the domain as it was entered or have it rewritten to either always or never include the www prefix.
Note: This setting does not apply for IP addresses and top‑level domains. |
Default page |
Allows you to redirect (permanent 301) all possible URLs that access the home page of your website to one single URL. Using a unified home page URL is highly recommended, because it prevents the duplicate content problem on your website's most important URL.
You can choose from the following options for the home page URL:
•Not specified - supports all possible home page URLs and does not perform any redirection. •Use domain root - always uses the base URL of the website's domain name. •Use page defined by default alias path - always uses the URL of the document specified by the website's Content -> Default alias path setting. •Use default page URL - always uses the default URL: <domain>/default.aspx
Important: This setting only works correctly if the website is hosted on IIS 7 or newer, and uses an application pool with an Integrated Managed pipeline mode. |
The options in this section are important when performing search engine optimization of multilingual websites. The following settings allow you to set up unique URLs for different language versions of pages in a search engine friendly format.
Force domain culture |
If checked, the system generates the domain name in document URLs based on the current content culture. Whenever a user switches to a different language on the website, the URL is redirected to the corresponding domain name.
You can assign cultures to domains by editing your site in Site Manager -> Sites:
•Set the culture of the website's main domain through the Visitor culture property on the General tab. •To define domain names for other languages, create Domain aliases with an appropriately set Visitor culture.
Note: You cannot use this option in combination with language prefixes. |
Use language prefix for URLs |
If enabled, the system generates document URLs with language prefixes. A language prefix is a subdirectory inserted into the URL. The name of the prefix matches the culture code (or culture alias) of the content culture selected on the website. |
Allow URLs without language prefixes |
If enabled, URLs without language prefixes are allowed. Otherwise the system redirects such URLs to a corresponding URL that includes a language prefix.
Only applies if Use language prefix for URLs is enabled. |
See also: