Google Sitemaps |
|
|

|
|
|
Google Sitemaps |
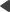
|
|

|
|
|
|
||
Kentico CMS allows you to automatically generate sitemaps for your websites according to the Google Sitemap Protocol. Sitemaps help search engines correctly index the content of websites and can have a significant effect on the resulting search ranking.
A sitemap is an XML file that lists the URLs of a website's pages along with additional metadata. Search engine crawlers (robots) use the sitemap data to determine which pages to index and how often to re-index pages. Sitemaps only serve as a recommendation and do not guarantee that all crawlers will index your website strictly according to the specified data.
For detailed information about the Sitemap protocol, see http://www.sitemaps.org/.
You can change the URL of your website's sitemap in Site Manager -> Settings -> URLs and SEO through the Google sitemap URL setting.
For example, the default value googlesitemap.xml means that web crawlers can access the sitemap through the following URL:
<website domain>/googlesitemap.xml
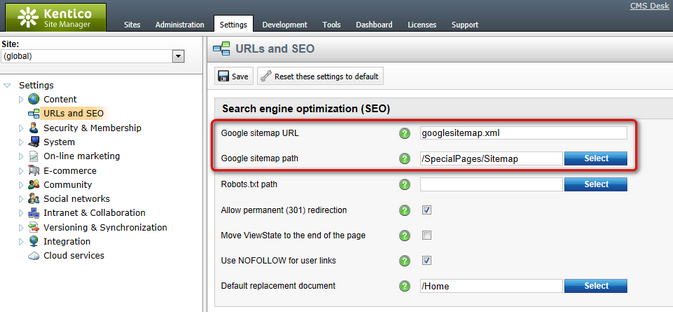
Sitemap-related website settings
|
Using the .xml extension
If you want to have your sitemap available under a URL with the .xml extension, you need to configure your application to handle all types of request extensions:
1.Edit your application's web.config file. 2.Find the system.webServer section directly under the web.config root (i.e. not under a specific <location> element). 3.Add the following attribute to the <modules> element:
|
The system generates sitemaps for websites based on the documents stored in the content tree.
By default the sitemap:
•Only contains pages (documents of the CMS.MenuItem type)
•Automatically excludes all pages whose parent document is not in the sitemap (such as pages stored under folders or custom document types)
You can modify the content of your website's sitemap by creating a dedicated sitemap document:
1. Add a new Page (menu item) document to your website's content tree.
oYou can use the predefined SEO -> Google Sitemap page template to quickly create sitemap documents. This template contains the required web part by default.
2. Place the Google Sitemap (XML Sitemap) web part onto the page.
oAdding this web part stops the page from displaying standard content. Instead, the page returns an XML response with the sitemap data.
oThe web part only generates output when the page is accessed on the live site.
3. Configure the content of the sitemap through the web part's properties.
oYou can limit which documents are included in the sitemap by entering an appropriate Path expression.
4. Go to Site Manager -> Settings -> URLs and SEO.
5. Enter the path of your sitemap document into the Google sitemap path setting.
The sitemap generated according to the configuration of the web part replaces the default sitemap. Search crawlers can access the sitemap either under the main URL specified in the Google sitemap URL setting, or directly through the URL of the document containing the Google Sitemap web part.
|
Customizing the default sitemap directly
If you do not wish to use portal engine pages and web parts, you can instead edit the markup of the ~/CMSPages/googlesitemap.aspx system page. This page generates the default sitemap for websites that have an empty Google sitemap path setting.
The GoogleSitemap control on the page provides the same configuration options as the Google Sitemap web part.
|
Troubleshooting:
If you encounter problems with pages missing in your sitemap, try checking for the following:
•Manually excluded documents - specific documents may be excluded through their sitemap properties (Show in sitemap or Exclude from search).
•Incorrect content filtering - review the content filtering properties of your Google Sitemap web part.
oIf the Document types property is empty, the sitemap only loads pages (CMS.MenuItem documents). Add the document types that you wish to have in the sitemap. You can use the asterisk (*) wildcard to specify all document types.
•Broken document hierarchy - sections of the website may be excluded due to parent documents missing in the sitemap. To load all documents regardless of the parent‑child hierarchy in the content tree, disable the Hide children for hidden parent property of the Google Sitemap web part.
By filling in the sitemap properties of documents, you can exclude specific pages from sitemaps or give search crawlers additional details describing how to index pages:
1. Select the document in the content tree of CMS Desk.
2. Open the document's Properties -> Navigation tab.
3. Set up the following properties:
Basic properties |
|
Show in sitemap |
Sitemaps only list documents that have this property enabled. |
Search & SEO |
|
Exclude from search |
Marks the document to be ignored by all forms of search, including search engines.
Enabling this checkbox excludes the document from sitemaps by default. However, individual XML Sitemap web parts can override this setting and generate sitemaps including documents that are excluded from search. |
Sitemap change frequency |
Determines the value of the document's <changefreq> tag in the sitemap. This metadata provides a suggestion to search engines about how often they should re-index the page.
Choose a value that reflects how frequently the page's content changes. |
Sitemap priority |
Allows you to inform web crawlers which pages you consider to be the most important.
The system converts the selected priority to a decimal number between 0 and 1 and adds the number as the value of the document's <priority> tag in the sitemap. Web crawlers only measure the priority in relation to other pages on the website. |
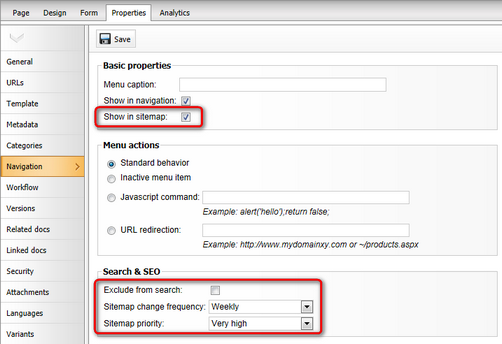
Setting a document's sitemap properties
If you enter the URL of the sitemap into your browser, you can review the generated XML output. The system automatically creates the required XML structure:

XML output of the Google sitemap generated for a Kentico CMS website
•The <url> elements represent individual pages.
•The sitemap loads the values of the <loc> and <lastmod> tags from the data of the corresponding documents.
•The <changefreq> and <priority> optional tags are added for documents that have values in their Sitemap change frequency and Sitemap priority properties.
A single XML sitemap can only list up to 50 000 pages (URLs). If you need to include more pages, prepare multiple sitemaps and create a sitemap index for your website:
1. Add any number of sitemap documents, each one containing its own Google Sitemap web part.
2. Separate your website's pages between the sitemaps by configuring the content filtering properties of the web parts.
oEach sitemap can contain a maximum of 50 000 items.
oAvoid duplicate content — do not list the same page URLs in multiple sitemaps.
3. Create the index as another document with a Google Sitemap web part.
oSwitch the Sitemap mode property of the web part to Sitemap index.
oConfigure the content filtering properties so that the sitemap index web part loads only the documents representing your sitemaps.
4. Enter the path of your sitemap index document into the website's Google sitemap path setting.
oThis ensures that crawlers process the sitemap index first.
The sitemap index points search engine crawlers to the other sitemaps, which then provide the lists of page URLs in the usual way.
If you need to override the default XML format of a sitemap or index, you can specify a custom transformation for the Google Sitemap web part or GoogleSitemap control. This allows you to react to any changes in the Sitemap protocol.
For example, the default CMS.Root.GoogleSiteMap transformation uses the following code to define the sitemap structure:
<url> |
The GetSitemapItem transformation method generates XML tags according to the sitemap protocol. The method's parameter specifies the type of the tag, and the value is dynamically loaded from the data of the transformed documents.
In the final XML output, the web part automatically encloses the transformed items within either a <urlset> or <sitemapindex> element depending on the selected Sitemap mode.