A/B testing overview |
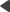
|
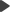
|

|
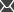
|
|
A/B testing overview |
|
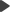
|

|
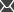
|
|
|
||
A/B testing is an on‑line marketing technique used to optimize the pages of a website according to the reactions of visitors. This is achieved by creating one or more modified versions of a given page and running them all at the same time during a designated testing period. The system then divides traffic between individual page versions and tracks how the changes affect the user experience and activity of visitors.
The following images show two versions of a sample home page — the original and an alternative page with the position of the left and right content columns reversed.
Some visitors will be assigned to the second version and will see the following when they view the home page:
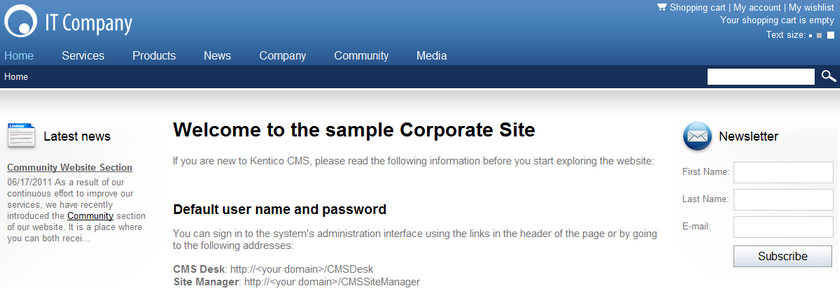
There are no limitations placed on the modifications that can be made to different page options. They may include anything from subtle changes to using a completely different page.
In Kentico CMS, the basic objects that provide this functionality are A/B tests, which can be created for specific website pages. The page options defined for a test are called Page variants. Each variant is linked to a document in the content tree of the website that can be designed and configured using the standard web development process. Usually, the Original page for which the test was created will be included as one of the variants, so that potential improvements can be compared with the baseline statistics (those of the unmodified page).
For a practical scenario, imagine that you have an e‑commerce page on your website where visitors can purchase products and you wish to fine‑tune it to be more user friendly in order to increase the amount of sales. By utilizing A/B testing, you can create multiple versions of this page with any type of modifications such as a slightly altered layout, graphical design or text content. These alternative pages will then serve as variants of the A/B test. While the test is running, it will automatically display different page variants to different visitors and keep track of all product purchases as conversions. When the test is completed after a certain amount of time, you can evaluate which page variant encouraged more users to make purchases on the website and set the most successful one as the permanent page.
Please see the Creating an A/B test topic for detailed information about how an A/B test can be defined for a page. The data gathered by A/B tests is displayed using reports that allow you to view and analyze several types of conversion metrics, as described in Analyzing A/B test results.
With A/B testing, results are tracked for entire page variants, which means that the measured statistics reflect the combined effect of all changes made to each variant. If you wish to monitor how individual page modifications affect the behaviour visitors, you may use Multivariate testing, which is another website optimization feature provided by Kentico CMS.
When a visitor navigates to a page that has a running A/B test defined, one of the page variants configured for the given test will be displayed to them. The variant is chosen randomly for every user. With a large enough visit sample size, each page variant should receive roughly the same amount of traffic during the course of the test.
A persistent cookie is stored in the visitor's browser, used to identify which variant was assigned by the given A/B test. The name of the cookie uses the following format: CMSAB<A/B test code name>. It saves the code name of the assigned page variant as its value. This cookie expires either within 30 days after the last visit on the tested page, or on the date when the test is configured to end.
Any conversions performed on the website by users who have passed through an A/B test page will be logged under the assigned page variant, which is taken from the value of the A/B testing cookie. The logging of conversion hits is provided by the Web analytics module. In addition to monitoring conversions, the cookie also ensures that returning visitors are always shown the page variant that was previously assigned to them, which helps avoid confusion by maintaining a consistent appearance of the tested page.
It is possible to run multiple A/B tests concurrently for different pages on the same website. Conversions will be logged for all tests defined for pages visited by a given user, according to the cookies present in the browser.