Developing custom filters |
|
|

|
|
|
Developing custom filters |
|
|

|
|
|
|
||
Filters are components that allow users to modify the data loaded and displayed by other website components. Filters provide two types of functionality:
•Limiting the range of items displayed in a list
•Changing the order of items in a list
Kentico CMS comes with a built-in set of filters for various types of data, but you can also create custom filters to fulfill specific requirements.
1. Implement filters as user controls that inherit from one of the following base classes:
•CMSAbstractDataFilterControl - works with document data sources
•CMSAbstractMenuFilterControl - works with navigation web parts
•CMSAbstractQueryFilterControl - works with custom table and query data sources
Select the appropriate base class according to the type of data that you need to filter. You can find these base classes in the CMS.Controls namespace.
|
Note
If you are connecting a CMSAbstractQueryFilterControl filter to a data source with a custom query, the query must contain the ##WHERE## and ##ORDERBY## expressions. When applied, the filter replaces the expressions with dynamically generated SQL code.
Query example:
|
2. Add the filter control onto your website through the Filter web part.
oYou need to specify the path to the .ascx file in the Filter control path property.
3. Attach the filter web part to the data source web part of the matching type.
You can also use custom filters anywhere in your code as standard user controls, for example on ASPX templates or in other web parts. All necessary properties, such as the FilterName used to connect with the data source, are inherited from the base class.
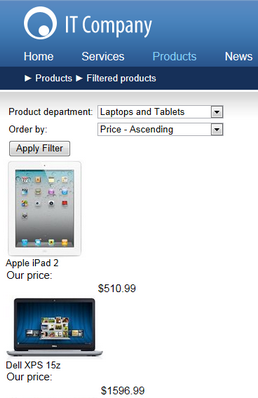
The example below demonstrates how to develop a custom filter. This sample filter works with product documents. It supports filtering according to product departments and allows the selection of several options that determine the order in which products are displayed. You can create filters for all types of documents or other objects using the same approach.
1. Open the web project in Visual Studio and create a New folder under the root called CMSGlobalFiles (if it doesn't already exist).
oThe content of this folder can be exported along with your site when it is deployed to the live server.
2. Add a new Web User Control named CustomProductFilter.ascx into the CMSGlobalFiles folder and modify it to contain the following code:
<%@ Control Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="CustomProductFilter.ascx.cs" Inherits="CMSGlobalFiles_CustomProductFilter" %> |
This creates the design of the filter's user interface. As you can see, it is composed of localized labels, drop-down lists and a button arranged in a simple table layout. Alternatively, it is possible to use a CSS‑based layout applied through HTML elements (e.g. <div>, <span>, etc.).
When developing a filter for actual live deployment, it may be preferable to enter the captions of the child controls using localization strings through the ResourceString property, rather than directly as Text.
3. Switch to the code behind file of the user control, add the references shown below and set the control to inherit from the appropriate base class. This example uses the CMSAbstractDataFilterControl class, since the filter is intended for use with a document data source.
[C#]
using System; |
4. Add the following methods into the user control class:
[C#]
/// <summary> |
These methods ensure that the correct filtering options are loaded into the child drop-down lists.
5. Define the SetFilter() method as shown below:
[C#]
/// <summary> |
The custom filter control dynamically generates a WHERE condition and ORDER BY statement based on the current filter selection, which is then used to set the value of the WhereCondition and OrderBy members inherited from the base class. These members are read by the data source to which the filter is attached and inserted into the SQL query used to load data. Remember that the filter must inherit from the appropriate base class according to the type of the used data source.
6. Add two more methods that override the handlers of the Init and PreRender events:
[C#]
/// <summary> |
The handlers ensure that the appropriate private methods (defined previously in the example) are called during the correct stages of the page life cycle.
When the Apply Filter button is clicked, a postback occurs, which triggers the SetFilter() method during the PreRender event and the filter is applied to the displayed data. Notice the use of the CMS.GlobalHelper.RequestHelper.IsPostBack() method in the conditions. The SetFilter() method is only called when the current page request is a postback and the child controls are initialized only when this is not the case.
The filter control is now finished and you can try out its functionality. It is recommended to test the filter on the Corporate or E-commerce sample sites, since they already contain examples of product documents.
Go to CMS Desk, create a new page and place the following web parts into its design:
Web part |
Instructions |
Documents data source |
1.Configure the web part to load product documents. 2.Fill in the Filter name property (e.g. CustomProductFilter).
Note: You can alternatively use the Products data source web part for this purpose. |
Filter |
1.Assign a Filter name that matches the data source (CustomProductFilter). 2.Enter the path of the .ascx file implementing your custom filter into the Filter control path property (~/CMSGlobalFiles/CustomProductFilter.ascx). |
Basic repeater |
1.Enter the ID of the Documents data source web part into the Data source name property. 2.Set an appropriate Transformation name, for example: Ecommerce.Transformations.Product_SimplePreview |
You can find more information about how this type of web part combination works in Using Data source web parts.
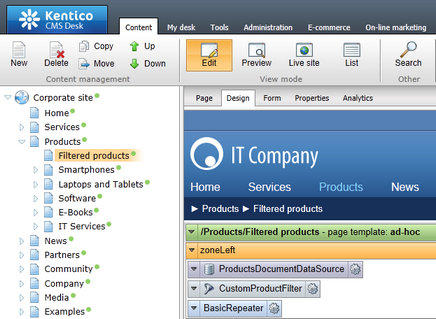
If you view the page in Live site mode, it displays a list of products with the custom filter shown above. You can filter the products by their department and change the order in which they are displayed.