Securing the CMSHelp folder |
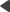
|
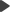
|

|
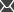
|
|
Securing the CMSHelp folder |
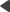
|
|

|
|
|
|
||
Kentico CMS comes with an on‑line help reference that is available in the database installer and most parts of the administration interface. Users can view it to access context‑specific information about the current section of the application's interface. By default, the HTML content of the on‑line help can be opened by any users (including public) if they enter the appropriate URL, which may not be desirable in certain scenarios, e.g. in the case of high‑security websites or if you are creating a rebranded solution.
There are several ways to solve this issue. The simplest is to delete the ~/CMSHelp folder from the project of your production website. This removes the possibility of public users opening the help files, but the on‑line help in the Kentico CMS administration interface will no longer be available.
If you wish to keep the on‑line help on your live website, you can limit access to the content of the help folder so that only users with the appropriate authorization will be able to view it. You can follow the steps below to perform the required configuration:
1. First, find the <system.webServer> section of your application in the web.config file. One option is to add the runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests attribute to the <modules> element as shown in the example below:
<system.webServer> |
Setting this attribute to true ensures that all requests will be processed by the application and will require authentication if needed.
Alternatively, if you do not want the application to process all additional request types, only .html and .htm, you can add the following two handlers into the <handlers> element:
<handlers> |
Adjust the path in the scriptProcessor attribute as necessary according to your specific environment.
2. Next, define the authorization rules that should be applied to the content of the CMSHelp folder. You can do so by adding the following section into your web.config file:
<location path="CMSHelp"> |
The example above will only allow authenticated users to access the on‑line help files, and public users will not be able to reach them through a direct URL without being prompted to log in. To further increase the security, you can restrict access only for a specific set of roles by editing the <authorization> section as shown below:
<authorization> |
Now only users who belong to the given roles (specified by their code names) will have access.