Where is the content stored? |
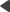
|
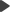
|

|
|
|
Where is the content stored? |
|
|

|
|
|
|
||
Kentico CMS provides a content management sub-system, also known as content repository, that allows you to organize website structure and content. Moreover, it provides a layer of security, workflow, versioning, search and other services. All types of content can be retrieved and modified through a single Application Programming Interface (API).
The following figure explains the difference between common data access approach and a content repository of Kentico CMS:
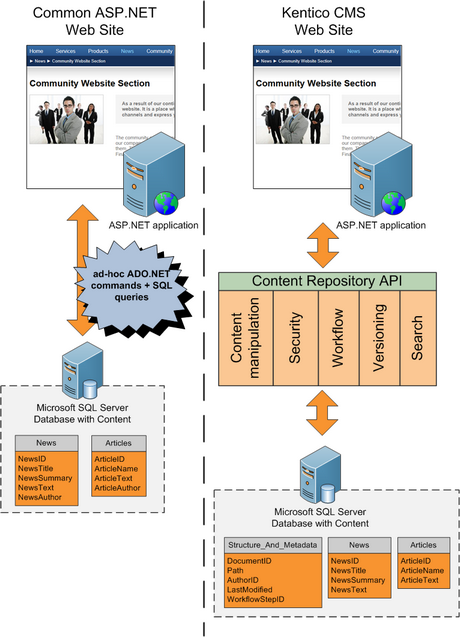
As you can see, a common approach to building dynamic websites is to write code for every page and every content type. It means that you need to write similar ADO.NET commands and SQL queries over and over again. With unified content repository, you use a complete set of API methods that allow you to save and retrieve any content type using methods someone wrote for you.
It greatly simplifies the management and retrieval of content since:
•you do not need to write your own methods, you only call API or use built-in controls
•same rules and mechanisms can be applied to any content type, without writing additional code for every new type
An important part of content repository is metadata. The metadata includes:
•content organization into a tree hierarchy that also represents the site map
•information about content authors and modifications
•workflow-related details, such as current workflow step
•content expiration
•permissions for the given document
In the example above, you can see that with classic approach, both News and Articles tables contain the attribute Author. In the content repository, the author is stored in shared metadata for all documents, regardless of their type.
|
Please note
All metafiles and attachments are stored under a folder specified in Site Manager -> Settings -> System -> Files -> Files folder. If this path is not set:
•metafiles of objects not connected with a particular site (global objects) are stored under <web root>/CMSFiles •metafiles of objects connected with a particular site are stored under <web root>/<site name>/metafiles •attachments (always connected with a particular site) are stored under <web root>/site name>/files |
As you can see, the content repository represents a systematic approach to content storage, manipulation and security.